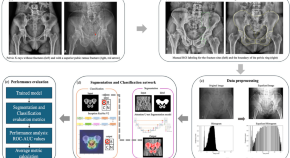
Image processing is manipulation of an image that has been digitised and uploaded into a computer. Software programs modify the image to make it more useful, and can for example be used to enable image recognition.

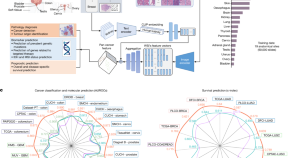
A study describes the development of a generalizable foundation machine learning framework to extract pathology imaging features for cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction.
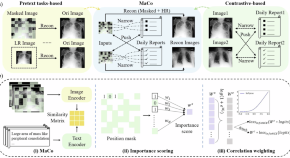
Multi-modal foundation models are increasingly important in medical applications. Here, authors show a masked contrastive chest X-ray model that achieves fine-grained image understanding and zero-shot capabilities, outperforming existing methods
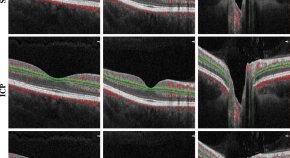
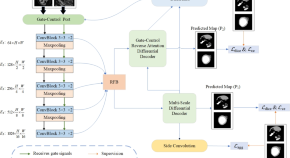
The identification of senescent cells is a long-standing unresolved challenge, owing to their intrinsic heterogeneity and the lack of universal markers. In this Comment, we discuss the recent advent of machine-learning-based approaches to identifying senescent cells by using unbiased, multiparameter morphological assessments, and how these tools can assist future senescence research.

The success of deep learning in analyzing bioimages comes at the expense of biologically meaningful interpretations. We review the state of the art of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in bioimaging and discuss its potential in hypothesis generation and data-driven discovery.
New approaches in artificial intelligence (AI), such as foundation models and synthetic data, are having a substantial impact on many areas of applied computer science. Here we discuss the potential to apply these developments to the computational challenges associated with producing synapse-resolution maps of nervous systems, an area in which major ambitions are currently bottlenecked by AI performance.
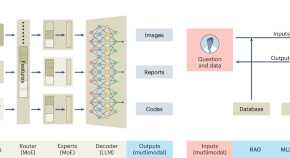
Multimodal large language models have been recognized as a historical milestone in the field of artificial intelligence and have demonstrated revolutionary potentials not only in commercial applications, but also for many scientific fields. Here we give a brief overview of multimodal large language models through the lens of bioimage analysis and discuss how we could build these models as a community to facilitate biology research.
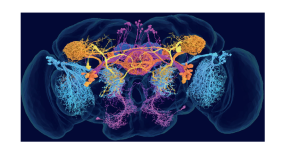
Machine learning approaches can distinguish six different classes of presynapses from electron micrographs across the Drosophila brain.